
Many moms worry about not pumping a normal amount of breast milk particularly when they are dependent upon pumping. It’s easy to compare yourself to others, or to feel discouraged if you don’t see large volumes of milk. But the truth is, there’s a wide range of “normal” when it comes to pumping output. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions and help you understand what to expect.
The “Normal” Breast Milk Output Range is Wide
There’s no single number that defines a “good” pumping session or how “good” your overall supply is. Factors like your baby’s age, time of day, how often you pump, and your individual body all play a role. Some moms might consistently pump several ounces per session, while others might only get a fraction of that. Both can be perfectly normal.
Exclusively pumping mothers: Seeing between 2-4 ounces combined from both breasts during a pumping session every 2-3 hours is often considered the high end of the pumping spectrum and reserved for moms who exclusively pump.
Mothers primarily breastfeeding / pump occasionally: Seeing smaller amounts, sometimes as little as 0.5 to 2 ounces per session, is completely normal for a mother only occasionally pumping. This is no reflection of an overall low milk supply.
Pumped Amount Isn’t a Direct Measure of Supply
It’s important to understand that pump output doesn’t always reflect your total milk supply. Babies are often more efficient at removing milk than pumps. If your baby is gaining weight well and producing plenty of wet and dirty diapers, you’re likely making enough milk, even if your pump output seems low.
Factors Affecting Breast Milk Pumping Output
Baby’s Age: In the early weeks, when your milk supply is still establishing, you might pump smaller amounts. As your baby gets older and your supply regulates, you might see an increase.
Time of Day: Milk supply is often higher in the morning. You might notice a difference in output between morning and evening pumping sessions.
Pumping Frequency: The more often you pump, the more milk you’ll likely produce. Regular and frequent milk removal signals your body to make more milk.
Pump Type and Fit: A good quality pump with properly fitted flanges is essential. A poor fit can significantly reduce milk output.
Stress and Relaxation: Stress can inhibit milk flow. Try to relax and create a calm environment before and during pumping.
Hydration and Nutrition: Staying well-hydrated and eating a balanced diet supports milk production.
Common Misconceptions
It’s completely normal to have concerns over your milk supply or to question whether or not your body is doing “enough.” This is commonly spurred along by misconceptions that permeate the breastfeeding world. Let’s clear up some of these points of confusion.
“If I don’t pump a lot, I don’t have enough milk.”
This is a common misconception. As stated before, pumping output is not a direct indication of your overall milk supply.
“Everyone else pumps more than me.”
Social media can create a false sense of what’s “normal.” Remember that everyone’s body is different. Try following some accounts of certified lactation consultants or breastfeeding experts.
“I need to pump a full bottle every time.”
This is not always the case. Small, frequent pumping sessions can be just as effective as longer sessions.
What to Focus On
Try to focus on the things that indicate the state of your breastfeeding journey. These things will also help you know how to adjust and change.
Baby’s Cues: Pay attention to your baby’s hunger cues and feeding behaviors.
Weight Gain and Diaper Output: These are the best indicators of whether your baby is getting enough milk.
Consistency: Pump regularly and consistently to maintain your milk supply.
Proper Pump Fit: Ensure your pump flanges fit correctly.
How Hygeia Health Can Help:
A quality breast pump can make a significant difference in your pumping experience. At Hygeia Health, we’re dedicated to providing moms with reliable and effective breast pumps, which can make a huge difference in your breastfeeding journey, especially if you are pumping to maintain your milk supply.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to get a 100% insurance-covered breast pump and make your breastfeeding journey smoother and more successful. Don’t let pumping output discourage you. Focus on your baby’s cues, and trust your body. Remember, you’re doing a great job!

Congratulations! You’ve reached the six-month mark in your breastfeeding journey. This is a huge accomplishment, and you and your baby have likely established a rhythm that works for you. But as your baby grows and develops, breastfeeding can change. This post will explore some common challenges and solutions for breastfeeding babies six months and older, and how a good breast pump can continue to support your journey.
Decreased Frequency of Feedings
As your baby starts solids, they may nurse less often. This is normal. Offer the breast before solids to ensure they are still getting the majority of their nutrition from breast milk. Continue to respond to their hunger cues, and don’t worry if the frequency changes.
Managing Distractions
Older babies are more aware of their surroundings. They might get distracted while nursing. Try breastfeeding in a quiet environment with minimal stimulation. You can also try nursing while your baby is sleepy or in a carrier.
Changes in Milk Supply
Your milk supply might adjust as your baby’s needs change. This is usually a natural process. Continue to nurse on demand and pump if needed to maintain your supply. If you have concerns about your milk supply, talk to a lactation consultant.
Returning to Work
If you’re returning to work, pumping becomes essential. Establish a pumping routine that mimics your baby’s feeding schedule. A good quality breast pump can make all the difference in maintaining your milk supply and making pumping at work more manageable.
Weaning
Some babies start to wean naturally around this age, while others continue to breastfeed for much longer. Follow your baby’s lead. If they are showing signs of weaning (like refusing the breast or being more interested in solids), respect their cues. If you want to continue breastfeeding, keep offering the breast and pumping as needed.
Teething
Teething can sometimes make breastfeeding uncomfortable. Offer your baby chilled teethers before nursing. If your baby is biting, gently break the suction and offer them a teether. Consistency is key.
Changes in Sleep Patterns
Sometimes, babies who previously slept well might start waking more frequently at night. This can be related to developmental leaps, teething, or simply wanting comfort. Offering the breast can be a soothing way to help them back to sleep.
The Importance of Continued Breastfeeding
Even as your baby explores solid foods, breast milk continues to provide essential nutrients, antibodies, and immune protection. The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding until at least two years of age, or for as long as mother and baby desire.
How a Breast Pump Can Help:
A reliable breast pump can be invaluable for mothers breastfeeding older babies. It can help:
- Maintain milk supply, especially when separated from your baby
- Provide expressed milk for when you’re away or if your baby needs extra
- Relieve engorgement
- Support your breastfeeding journey as your baby grows and changes
At Hygeia Health, we understand the importance of having a quality breast pump. All moms should have access to one, and that’s why we help moms get a 100% insurance-covered breast pump. A reliable breast pump can make a huge difference in your breastfeeding experience, especially as your baby gets older and your needs change.
Breastfeeding beyond six months is a remarkable achievement. While there may be challenges, remember that you and your baby are a team. Trust your instincts, seek support when needed, and enjoy this special time.

Navigating the early days of breastfeeding can be overwhelming, especially for a mom who finds herself in the dreaded “pump trap” when trying to manage engorgement and proper milk supply. Understanding how your body regulates milk production is key to a successful breastfeeding journey.
Breast milk is packed with antibodies, nutrients, and everything your little one needs to grow and thrive. One of the most fascinating aspects of breastfeeding is how your body knows exactly how much milk to make. This is all thanks to a complex system of hormones and feedback loops. Understanding how breast milk supply regulation works can help you feel more confident in your breastfeeding journey.
This post will break down the fascinating science behind milk supply, explain how to avoid the “pump trap” that can exacerbate engorgement, and offer tips for managing your milk production long-term.
What to know about establishing your supply
The first few weeks after birth are crucial for establishing a good milk supply. Your body works on a supply-and-demand system. The more frequently and effectively your baby nurses, or you pump, the more signals your body receives to produce milk. This is why frequent milk removal is so important, especially in the early days.
It’s important to remember that your body is designed to regulate milk production; you’re not solely responsible for making it happen. Hormones play a crucial role. Prolactin, the “milk-making” hormone, is released when your baby nurses. More prolactin means more milk. Oxytocin, sometimes called the “love hormone,” is also released during breastfeeding. It triggers the muscles around the milk glands to contract, helping milk flow—this is the “let-down” reflex.
What to know about the role of feedback loops
Your body uses feedback loops to fine-tune milk production. Imagine it like a thermostat. When your baby nurses or you pump, milk is removed from your breasts. This signals your body to produce more milk to replenish the supply. The emptier your breasts become, the stronger the signal to make more milk. Conversely, if your breasts are full, your body receives signals to slow down production.
This is why it’s important to breastfeed or pump frequently and on demand, especially in the early weeks. Responding to your baby’s hunger cues and allowing them to nurse for as long as they want helps establish a strong milk supply. It also helps to avoid supplementing with formula unless medically necessary, as this can interfere with your body’s natural supply-and-demand system.
What is the “pump trap” and how to avoid it
The ‘pump trap’ happens when a mom is pumping to relieve engorgement, but it becomes a never-ending cycle because the body continues overproduce.
While many moms worry about producing enough milk, the pendulum swings both ways as oversupply and engorgement can also be a challenge. Engorgement can be very uncomfortable, potentially leading to problems like mastitis, and making it difficult for babies to latch.
Frequent feedings or pumping sessions are crucial for establishing a healthy milk supply, but they can also contribute to overproduction, especially when pumping for relief. While your baby’s cues will tell you when they’re finished feeding, pumping requires you to decide when to stop. Completely emptying your breasts with each pumping session signals your body to continue producing large amounts of milk. If you’re experiencing oversupply, the key, is to avoid completely draining your breasts when you pump.
It is also important to note that if you pump before breastfeeding in order to relieve engorgement and tightness in your breasts, express only enough milk to allow your baby to latch comfortably.
How to best manage long-term milk supply
As your baby grows and their feeding patterns change, your milk supply will adjust accordingly. Your body is remarkably adaptable and can meet your baby’s changing needs. Even if you experience a temporary dip in supply due to illness, stress, or changes in routine, your body can usually bounce back with consistent milk removal.
There are several factors that can influence milk supply and it is valuable to be aware of them as a means of knowing what can help you manage over or under supply.
Frequency of milk removal: As mentioned already, frequent breastfeeding or pumping will help your body increase supply.
Effectiveness of milk removal: Ensuring your baby is latching properly or that your pump is working efficiently is crucial.
Hydration and nutrition: Staying well-hydrated and eating a healthy diet supports milk production.
Certain medications: Some medications can interfere with milk supply. Talk to your doctor about any medications you’re taking.
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid problems or retained placental fragments, can affect milk supply.
When to seek help
It’s important to also know that breast engorgement is not always a sign of oversupply, so if you are experiencing engorgement but feel it isn’t due to oversupply don’t hesitate to reach out to a lactation consultant or your healthcare provider. They can assess your situation and provide personalized guidance and support. They can help you optimize your breastfeeding technique, address any underlying issues, and develop a plan to boost your milk supply if needed.
We’re Here to Support You:
Having a reliable and easy-to-use pump can be a tremendous relief to a mom as she helps her body regulate milk supply, especially in the early weeks. We’re committed to supporting breastfeeding mothers in all aspects of the journey and even offer a way for moms to get a 100% insurance covered breast pump.
Our high-quality breast pumps are designed to make pumping easier and more efficient so that, in the end, you have a way to get your one-of-a-kind milk to your baby. To apply for a 100%-insurance-covered breast pump, simply visit our website and fill out the application form. We’ll review your application and contact you with the next steps.

Bringing your baby home is an exciting time, but it can also be filled with anxieties, especially when it comes to breastfeeding. You might be wondering, ‘When will my milk come in?’ and feeling anxious if it doesn’t seem to be flowing immediately. Rest assured, your body is working hard behind the scenes!
This blog post will explain what’s happening in those crucial early days, why your milk supply may not be abundant right away, and what your baby actually needs in the first few days after birth.
Understanding Colostrum
The first thing to put your mind at ease it to understand that milk is not the first thing your baby needs to consume after birth. In their initial days, your breasts produce colostrum, a thick, yellowish fluid packed with nutrients and antibodies. Think of it as liquid gold for your baby! This precious first milk is all your newborn needs in those early days.
With that, it’s important to not fret over the small amount of colostrum your body is producing. Colostrum is incredibly concentrated and your baby’s tiny stomach doesn’t need much. It’s completely normal to produce only small amounts of colostrum in the first few days. Focus on frequent feedings and observe your baby’s cues.
Maximizing Skin-to-Skin Contact
Skin-to-skin contact is crucial during the first days of your baby’s life. Holding your baby against your bare chest helps regulate their temperature, promotes bonding, and encourages frequent breastfeeding, which can also trigger milk production.
Skin-to-skin contact stimulates the release of oxytocin, a hormone crucial for both milk production and bonding. Oxytocin helps contract the muscles around the milk-producing glands, facilitating milk ejection, also known as let-down. It also stimulates the release of prolactin, another important hormone for milk production.
Additionally, implementing skin-to-skin contact immediately after birth can encourage early latching. With skin-to-skin time, your baby is more likely to instinctively crawl towards the breast and latch naturally. This experience also helps the baby learn to recognize and respond to hunger cues, leading to more effective feeding.
Waiting on Milk to Come In with Rest and Recovery
It can take 3-5 days for your milk to come in after you’ve given birth. During this time, it’s crucial to avoid stressing about your milk supply and instead rely on the colostrum while you rest. Rest is essential for both you and your baby. Allow yourself time to recover from childbirth and focus on bonding.
The onset of milk production is often indicated by changes in your breast temperature, milk leakage, and breast fullness or engorgement. The experience varies among mothers, with some experiencing a gradual increase in milk production, while others may experience a more sudden “let-down.” This timeframe is a general guideline, based on the experiences of many mothers. If you have any concerns once you’re home, it’s important to consult with your doctor or a lactation consultant.
Maintaining Hydration and Nutrition
In addition to rest, hydrating and nourishing your body is crucial for milk production.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Keep a water bottle handy at your bedside, especially in the hospital.
Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet that includes:
Fruits and vegetables: Load up on colorful produce to provide essential vitamins and minerals.
Protein: Include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, and lentils.
Whole grains: Choose whole-grain options like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread for sustained energy.
Remember that your appetite may fluctuate in the early days. Listen to your body’s cues, but make an effort to eat nutritious foods to support your milk supply.”
Supporting Your Breastfeeding Journey
Milk supply can be a concern for many new mothers. At Hygeia Health, we understand that breast pumping can effectively stimulate milk production. Frequent pumping sessions, ideally every 2-3 hours, mimic a newborn’s feeding pattern and signal your body to increase milk production. This consistent stimulation helps to establish and maintain a good milk supply.
While pumping can be a valuable tool, direct breastfeeding remains the most natural and efficient way to stimulate milk production and build a strong bond with your baby.
Our high-quality breast pumps are designed to make pumping easier and more efficient so that, in the end, you have a way to get your one-of-a-kind milk to your baby. To apply for a 100%-insurance-covered breast pump, simply visit our website and fill out the application form. We’ll review your application and contact you with the next steps.
These early days are a precious time for you. Focus on bonding with your baby, and trust your body to do what it was made to do.

Nearly every part of parenthood has its ups and downs and breastfeeding is no exception. While it can be beautiful and rewarding, it is suddenly tough when your baby refuses the breast. It can be frustrating and disheartening. Just remember, you are not alone and there are strategies for overcoming the challenge of breast refusal.
This blog post will dive into the solutions to help you overcome this hurdle and get your breastfeeding journey back on track.
Understanding the Reasons for Breast Refusal
First, there are several reasons why a baby might refuse the breast, and it is important to understand where baby may be coming from in his or her refusal.
Painful latch: If your baby is experiencing pain while latching, they may refuse to breastfeed.
Tongue-tie or lip-tie: These conditions can make it difficult for your baby to latch properly and you may need to pursue treatment.
Illness: Do you lose your appetite when sick? Baby is no different. If your he or she is sick, they may be less interested in breastfeeding.
Distractions: Noise, light, or other distractions can interfere with breastfeeding. If you are trying to nurse with a cover, this can sometimes be problematic for baby’s attention also.
Stress or Overwhelm: Both you and your baby can experience stress, which can impact breastfeeding. It can impact baby’s ability to latch and your milk production.
Tips for Overcoming Breast Refusal
Identifying the possible cause of the issue can set you on track for which solution will help you overcome the obstacle.
Consult a Lactation Consultant: A lactation consultant can assess your baby’s latch and offer personalized advice.
Skin-to-Skin Contact: Spend quality time skin-to-skin with your baby. The direct physical contact can help calm them and encourage them to latch.
Try Different Positions: Experiment with different breastfeeding positions to find what works best for you and your baby.
Express Milk: If your baby is refusing the breast, you can express milk and feed it to them with a bottle or syringe or small spoon. With clean hands, you can even try using your pinky finger dipped in milk to feed baby.
Avoid Pacifiers: Using a pacifier can interfere with breastfeeding if your baby is already struggling with nursing.
Be Patient: Be patient and persistent. It may take time for your baby to adjust.
Tips for Returning To Breast after Bottle
Choose the Right Time: Try to breastfeed your baby when he or she is calm and relaxed, such as before a nap or bedtime.
Start Slowly: Begin by offering the breast for short periods, gradually increasing the duration as your baby gets used to it.
Express Milk and Offer It: Expressing some milk and offering it to your baby using a syringe, a spoon, or your finger as you hold them skin to skin can help them associate the taste of breast milk with your breast.
Be Patient: It may take several attempts for your baby to adjust to breastfeeding once he or she has taken to feeding from a bottle. Don’t get discouraged.
Hygeia Health: Supporting Your Breastfeeding Journey
At Hygeia Health, we know challenges like breast refusal are real for both first-time and seasoned mothers. Our high-quality breast pumps are designed to make pumping easier and more efficient so that, in the end, you have a way to get your one-of-a-kind milk to your baby.
To apply for a free breast pump, simply visit our website and fill out the application form. We’ll review your application and contact you with the next steps.
Remember, you’re not alone. With patience, persistence, and the right support, you can overcome breast refusal and enjoy the benefits of breastfeeding.
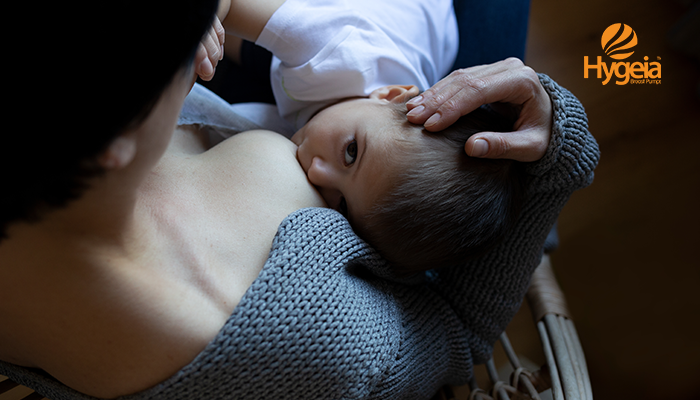
Breastfeeding: It’s like a superpower for moms. But sometimes, even superheroes need a boost. Some moms face the challenge of low milk supply, which may feel like losing one of your most important motherhood superpowers.
Don’t worry, it’s not just you! Many moms have been there, and there are ways to boost your milk production. Here are some tips to help you increase your breast milk production.
Your body needs encouragement
Feed Frequently: You may be exhausted and it’s not what you want to hear, but frequent feedings may be the solution. The more often you feed your baby, the more milk your body will produce. Try to feed on demand, whenever baby shows signs of hunger.
Skin-to-Skin Contact: Keep baby close! Skin-to-skin contact can help stimulate your milk production and promote bonding with your baby.
Pumping: If you’re pumping, make sure you’re using a good-quality pump and pumping frequently. You may also want to try pumping on both sides at the same time. This can be especially helpful if you are working or have to be away from baby for long periods of time. Check out the Hygeia Express breast pump.
Self-Care: Take care of yourself
Relax and Reduce Stress: What new mom isn’t stressed? And unfortunately that stress can impact your milk supply. Ask your support system to help you find ways to relax. Many people can manage stress through techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Get Enough Rest: While frequent feedings and pumping may make this a hard one, solid rest and sleep will help your body with milk production. Be assured that the messes, dirty dishes, and laundry can wait and give yourself permission to sleep when the baby sleeps.
Eat a Healthy Diet: Your milk is directly impacted by the foods you consume and how much water you are drinking. Eating a healthy, balanced diet can help support your milk production, so don’t rely on processed, low calorie foods. Make sure you’re getting enough calories, fluids, and nutrients.
Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Fluids matter but which fluids matter too, as the wrong ones will definitely create a lack of milk supply. Excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption can reduce your milk production, so reduce or avoid them completely.
Outside Help
Seek Support: If you’re struggling to increase your milk supply, don’t hesitate to seek support from a lactation consultant or breastfeeding support group.
Get a Free Breast Pump: We believe that every mother should have access to the tools and support they need to breastfeed their baby. That’s why we offer an insurance-covered breast pump to mothers qualify. To apply, simply fill out the application form. We’ll review your application and contact you with the next steps.
Hygeia Health Can Help: At Hygeia Health, we understand the importance of breastfeeding and the challenges that mothers may face. In addition to our high-quality breast pumps, we also offer resources and support to help mothers on their breastfeeding journey. Take advantage of our website and our customer service team.
You Can Do It
Increasing your milk supply takes time and patience. But with the right support and strategies, you can achieve your breastfeeding goals.






